Humanoid robots are a fascinating blend of technology and creativity—designed to mirror the complexity and wonder of the human body. Join us on this journey as we explore the essential components, advanced technology, and engineering behind these amazing creations.
The Building Blocks of Humanoid Robots
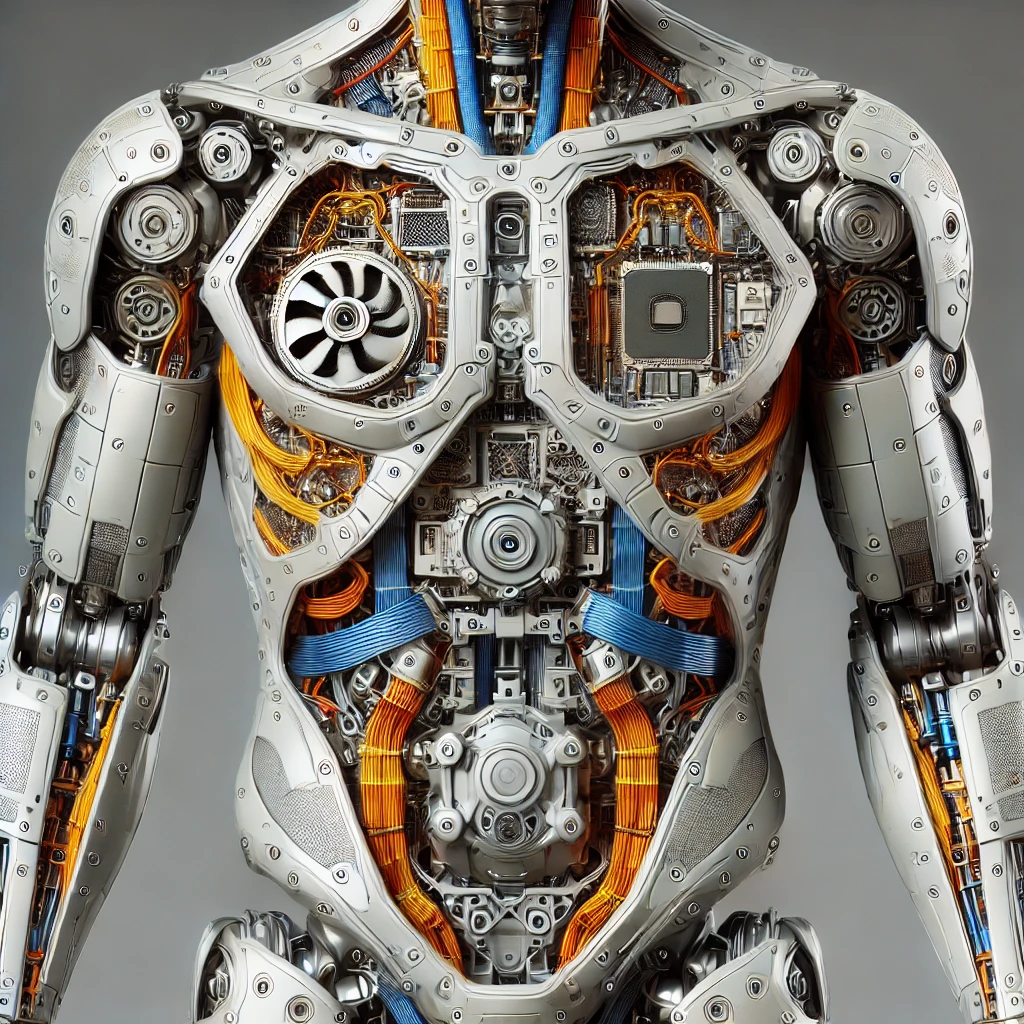

Torso
The central body supporting other components.
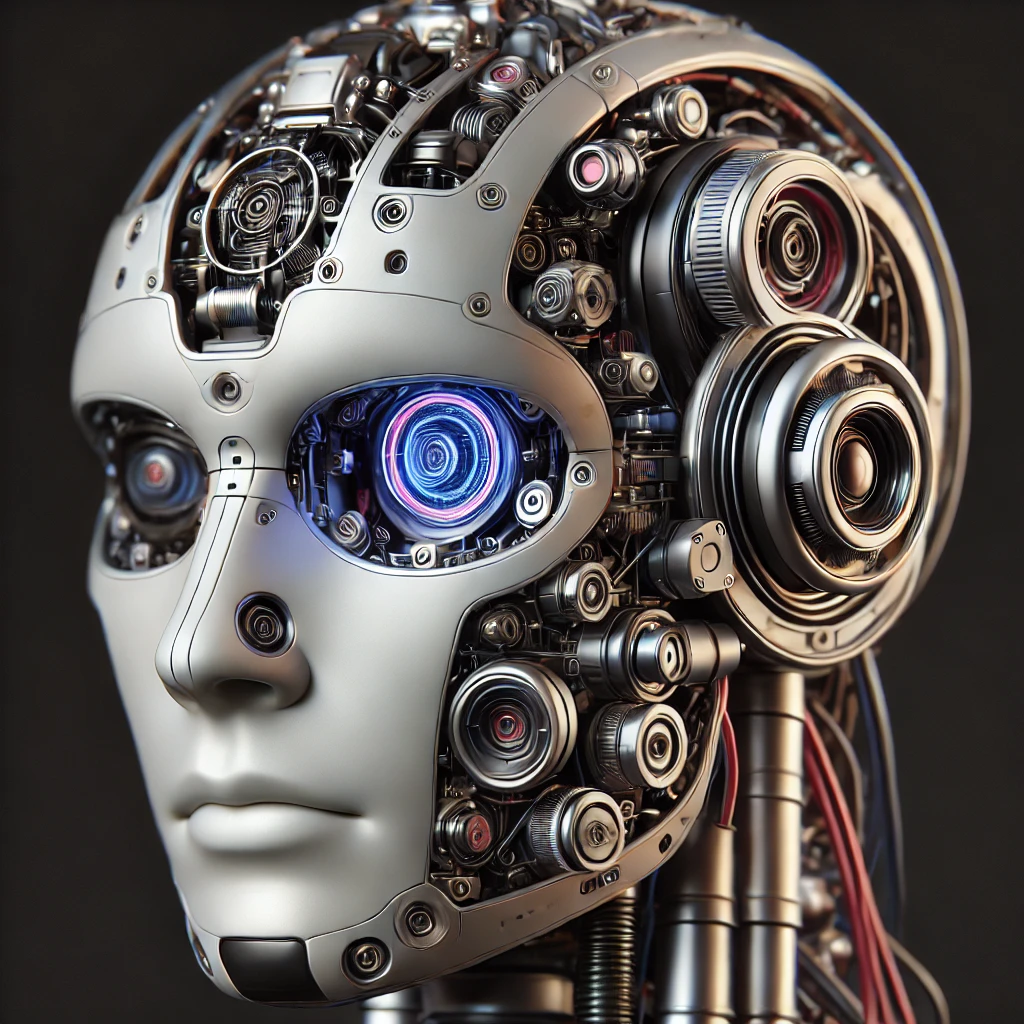
Head
Often includes sensory and control systems.
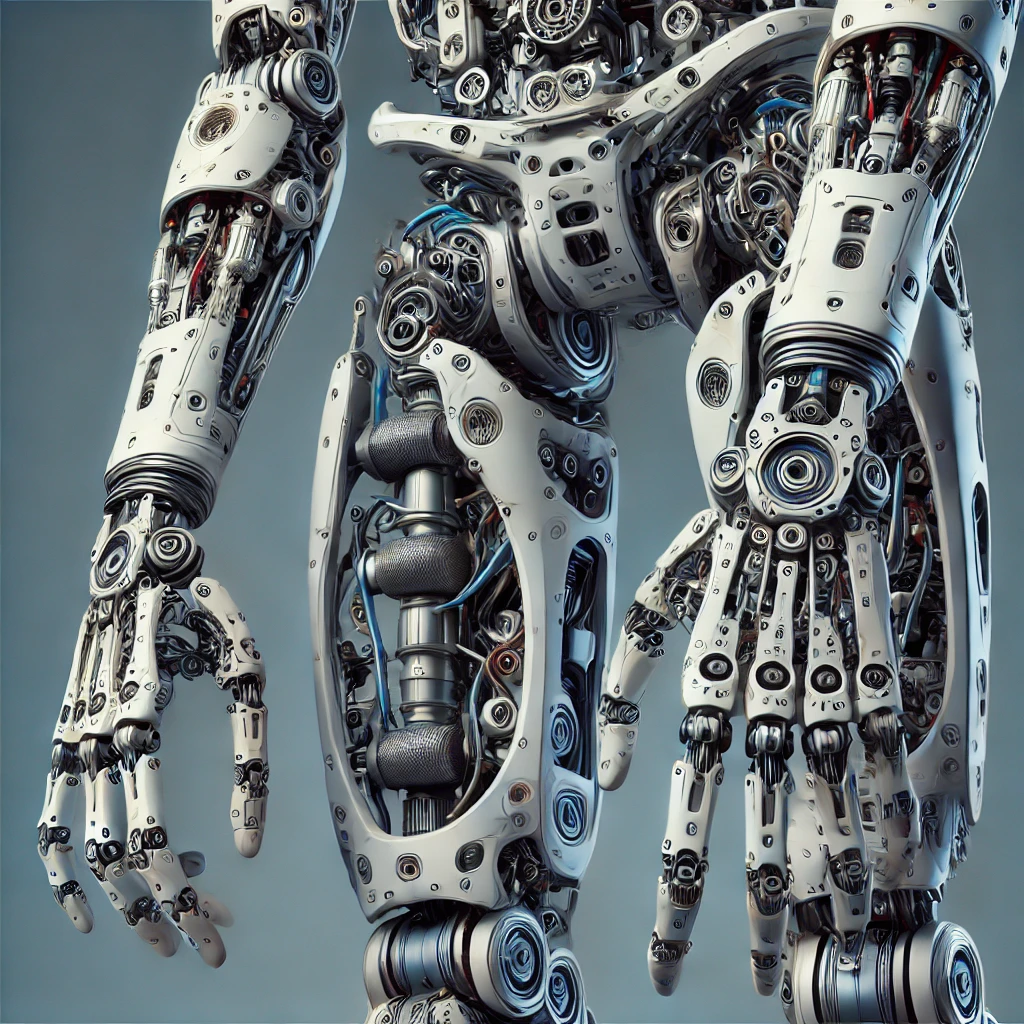

Arms and Legs
These provide human-like movement, enabling the robot to interact with its environment.
💡 Did You Know? Some robots replicate only part of the human body, while others strive for complete human-like realism!
Sensory Systems: Understanding the World
To interact with the environment effectively, humanoid robots rely on sophisticated sensory systems, much like our own senses.
Accelerometers
for measuring acceleration and understanding movement.
Tilt Sensors
to determine orientation.
Force and Position Sensors
to monitor contact and position within an environment.
Tactile Sensors
that detect touch and pressure.
Vision Sensors
like CCD cameras, serve as the robot's eyes.

Sound Sensors
like microphones to capture environmental noises and speech.
Actuators: The Muscles of a Humanoid
Actuators play a critical role in replicating human movement. Think of them as the muscles of a robot, driving the motion
Electric Actuators
are popular for their precision and compact size.

Pneumatic and Hydraulic Actuators
use air or fluid pressure, providing powerful and flexible motion.
Each actuator type has advantages and trade-offs, affecting a robot’s ability to achieve human-like motions.
💪 Movement Matters: Each actuator type has strengths that influence how the robot moves, allowing them to perform anything from delicate gestures to powerful actions.
Movement and Control: Joints at Work
Humanoid robots rely on a network of joints to achieve realistic, human-like motion:

Prismatic Joints
provide linear motion.

Revolute Joints
enable rotation, similar to how human elbows and knees work.

Spherical Joints
offer flexibility in multiple directions, similar to our shoulders and hips.
🔄 Sophisticated Movement: These joints, paired with intelligent control algorithms, help humanoid robots avoid obstacles, plan movement paths, and execute complex actions seamlessly.
Powering the Future: Energy Behind the Scenes
Humanoid robots need efficient power systems. Advanced batteries and energy management technology allow these robots to match human energy requirements while maintaining agility and lightness.
⚡ Fuel for Motion: Power systems are key to making humanoid robots dynamic and capable of extended activity.
The Choice of Materials
The materials used to build humanoid robots must balance strength, flexibility, and weight. Typical materials include:
- Lightweight Alloys for structural integrity.
- Composite Materials that offer high strength-to-weight ratios.
- Specialized Polymers for added flexibility and durability.
Wrapping up
The anatomy of a humanoid robot is a marvel of engineering—powered by sensors, actuators, and sophisticated AI systems. As technology advances, we move closer to creating lifelike robots that blur the line between humans and machines.
✨ Stay Connected: Follow HumanoidHub for more insights, latest breakthroughs, and captivating updates about humanoid robotics!

